Leaky Gut: What It Is and How to Heal It
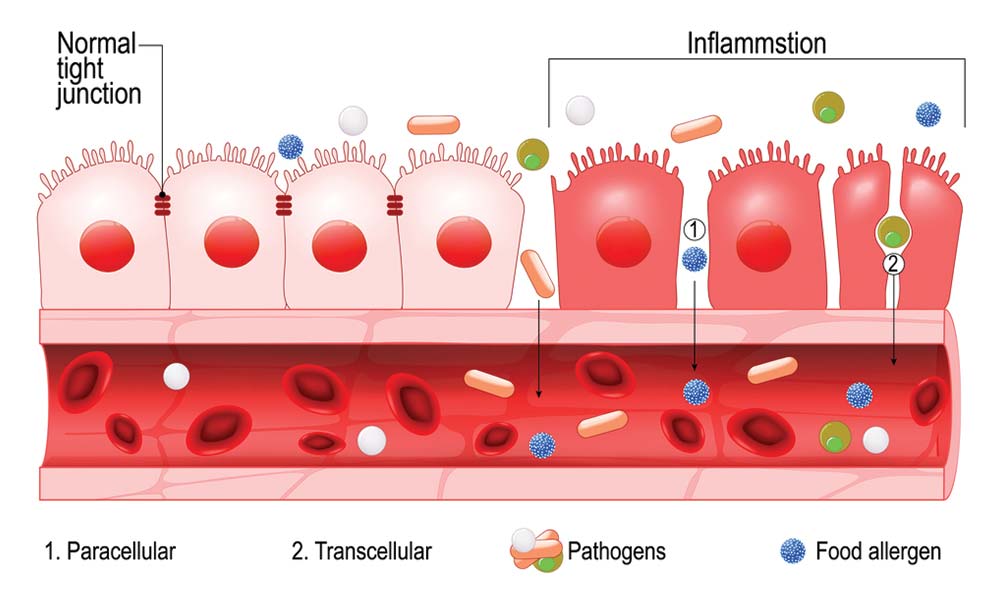
What Is Leaky Gut?
Leaky gut is a condition of the digestive system in which bacteria and toxins leak out through the walls of the intestines into the bloodstream. When it is working correctly, the lining of the intestines forms a barrier that allows helpful substances to be absorbed in the bloodstream, while blocking harmful substances.
There are naturally occurring gaps in the wall of the intestines that allow for some intestinal permeability. When these gaps are small, they are called tight junctions and form a barrier that only allows certain substances to pass through. However, when the gut lining in unhealthy, those gaps can become larger, allowing space for unwanted things like partially digested food particles, certain proteins, and toxins to enter the bloodstream. This is called increased intestinal permeability. The passage of harmful substances creates a cycle of inflammation and changes to gut bacteria. This cycle is associated with a number of chronic diseases.
What Are the Symptoms of Leaky Gut Syndrome?
Leaky gut syndrome is not recognized as an official condition my some doctors and can be difficult for all healthcare providers to identify. The symptoms often look very similar to other health conditions, so it is hard to distinguish the underlying cause. Constipation, bloating, and chronic diarrhea are leaky gut symptoms that also show up in numerous gastrointestinal illnesses and conditions. Nutritional deficiencies are also often seen. Fatigue, headache, trouble concentrating, and confusion, are vague and hard-to-diagnose symptoms. Widespread inflammation, joint pain, and skin conditions like eczema, rashes, and acne are associated with leaky gut but can also have a variety of other causes.
Is Leaky Gut a Cause or Symptom of Disease?
There is still a lot that science and doctors need to learn and understand about leaky gut. This includes whether leaky gut is the cause or symptom of certain diseases. While there is still much research to be done, there is some evidence that leaky gut is at least a precursor, if not a cause, to certain diseases like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and type 1 diabetes.
There is also evidence of the importance of gut health for maintaining health in other areas of the body besides the digestive tract. When the balance of bacteria in the gut is disrupted, it can lead to increased intestinal permeability which can release substances into the bloodstream which travel throughout the body. Again, the specific cause is not known, but some risk factors like autoimmune disorders, stress, poor nutrition, and excess consumption of alcohol have been identified.
Another fascinating area of research is the connection between the gastrointestinal tract and the brain. This is called the gut-brain axis. While much more research still needs to take place, some research indicates that leaky gut may contribute to depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues. This has the potential to create a new understanding of mental health issues, and revolutionary approaches to treatment.
Diseases Associated With Leaky Gut
There are some common digestive diseases as well as diseases found in other parts of the body that are often associated with leaky gut. These include conditions like Celiac Disease, Crohn’s Disease, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), as well as diabetes and liver disease. Many of these are considered autoimmune diseases or contain an autoimmune component. Autoimmune responses have been shown to be made worse by the presence of harmful substances that enter the bloodstream from the intestines. When these substances cross the intestinal barrier, the body recognizes them as foreign or harmful objects to be attacked through an immune response. Food allergies are another condition associated with leaky gut that can result in digestive issues and serious health problems. Heartburn, acid reflux and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) commonly occur due to food allergies and food sensitivities.
The immune system is also central to preventing other serious diseases like colon cancer. While research is still underway, scientists do know that the immune system is directly influenced by the makeup of the microbes and bacteria in the gut. There is a connection to be made and better understood the importance of maintaining a healthy digestive system, even in relation to causes and risk factors for serious diseases such as cancer.
Again, a lack of conclusive research limits our understating of the cause and effect relationship. But don’t be discouraged. While there is not a specific treatment for leaky gut syndrome, there are steps you can take to improve your gut health and remedy the symptoms attributed to leaky gut.
How to Improve Your Gut Health
Understanding and acceptance of leaky gut syndrome is growing. Researchers have found evidence of leaky gut’s existence, as well as indications that it contributes to a variety of health issues. However, the research is limited, and many doctors still do not consider leaky gut to be a legitimate medical issue. Because of the work yet to be done, there is no standard diagnosis and therefore no standard treatment. This has caused some people to explore natural or alternative medicine approaches. However, there are doctors like those at Gastroenterology Associates of Savannah, who understand the research and its limitations, but are committed to finding a solution to the symptoms you are experiencing.
There is no one proven method for completely healing the symptoms of leaky gut. But there are ways to improve gut health which is known to be good for overall health. And taking action to improve gut health may also relieve symptoms associated with leaky gut syndrome. An important first step is to make sure to address any known underlying or associated conditions.
There are also practical changes you can make to your daily habits to improve your gut health. Beneficial lifestyle changes include reducing stress which contributes to inflammation in the body. Consistent quality sleep and regular exercise are also both very important to gut health and other systems in your body. Finally, don’t smoke. If you are a smoker, make it your priority to find the support you need to help you quit.
Nutrition is another area vital to the health of your digestive system. Eat a well-balanced diet that incorporates lots of fruits and vegetables. Foods with prebiotic fiber (think vegetables and whole grains) are also important to help protect the good bacteria in your gut. What should you eat less of? It’s generally good nutritional practice to consume less sugar and sweeteners, as well as less dairy, eggs, and meat.
Probiotics encourage the growth of good bacteria and help with the balance of bacteria in your gut. Probiotics can be consumed through whole food sources or by taking supplements. Both sources help increase the good bacteria in the gut which aids in digestion, immunity, and other body functions. Antibiotic medications are known for upsetting the balance of bacteria in the gut. While destroying bad bacteria to help cure illnesses, antibiotics also wipe out the good bacteria. Avoiding unnecessary use of antibiotics, as well as taking a probiotic supplement after a round of antibiotics, will help restore the balance of good bacteria in your gut.
Have questions about leaky gut or other digestive conditions? The doctors at Gastroenterology Consultants of Savannah are here to listen and to assist you in finding answers. We are committed to helping our patients achieve and maintain optimal gastrointestinal health, and would love to partner with you to address your health concerns. Contact us today.